hOAT1 (SLC22A6)
➦ The human organic anion transporter 1 (OAT1; SLC22A6) is highly expressed at the basolateral membrane of proximal tubule cells in human kidneys. There OAT1 mediates the transport of numerous endogenous and exogenous compounds like antibiotics, diuretics, NSAID (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), antivirals, cytostatics and toxins. OAT1 facilitate the first step uptake at basolateral membrane of proximal tubule cells for renal secretion of a huge number of substrates. Therefore, the regulatory agencies decided that drugs eliminated significantly via the kidney have to be tested as potential inhibitors (substrates) for hOAT1.
| Main localization: | Kidney |
| Transporter assay: | Uptake transporter assay (potential inhibitors or substrates) |
| Probe substrates: | p-Aminohippuric acid (PAH) |
| Probe inhibitors: | Probenecid, glibenclamide |
| Regulatory relevance: | FDA and EMA guidance |
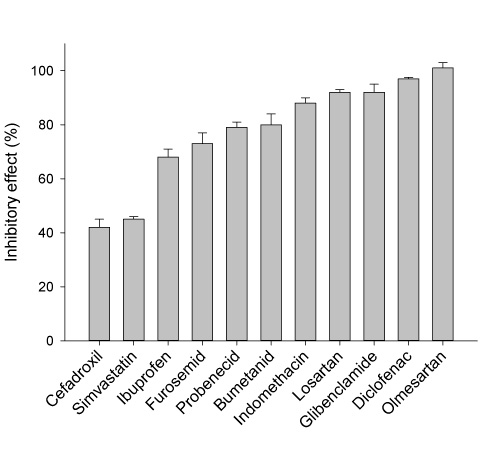
| Important interacting drugs: | Adefovir, acyclovir, methotrexate, ochratoxin A, olmesartan, probenecid, bumetanide, diclofenac, fluvastatin, furosemide, ibuprofen |
| From other species: | rOat1, mOat1 |
➦ Inhibition of hOAT1 mediated PAH uptake by different drugs (100 µM)