Methods
➦ Using genetically modified human kidney cells we provide interaction studies of drugs with specific transporter proteins. Because of regulatory guidelines (FDA, EMA, PMDA), the characterization of clinically relevant drug transporters is gaining an increasing importance during drug approval process.
To characterize drug transporter interaction we provide the following assays:
Inhibition Assay
 Probe substrate (radio-labeled, non-labeled, fluorescent)
Probe substrate (radio-labeled, non-labeled, fluorescent)
 Test item as an inhibitor
Test item as an inhibitor
Substrate Assay
 Test item as a substrate (radio-labeled, non-labeled, fluorescent)
Test item as a substrate (radio-labeled, non-labeled, fluorescent)
 Probe inhibitor
Probe inhibitor
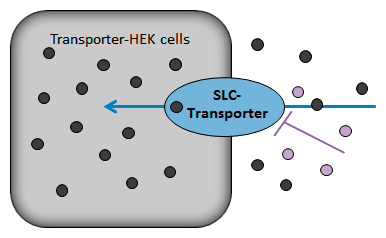
Uptake transporter assay for all SLC-Transporters
HEK cells stably expressing one specific uptake (SLC-) transporter are used as cell monolayers to investigate the uptake (accumulation into the cell) of a substrate (Probe substrate or test item) in the absence and presence of an inhibitor (Probe inhibitor or test item).
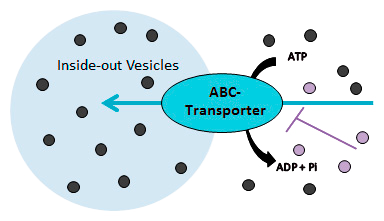
Vesicle based transporter assay for MDR1, BCRP, BSEP and MRPs
Membrane vesicles (inside-out orientated) prepared from transporter-HEK and control-HEK cells are used to measure the ATP-dependent direct uptake of a substrate (Probe substrate or test item) in the absence and presence of an inhibitor (Probe inhibitor or test item) by rapid filtration method. Vesicles are best suited for low permeability substrates because of poor retention of moderate-to high permeability compounds.
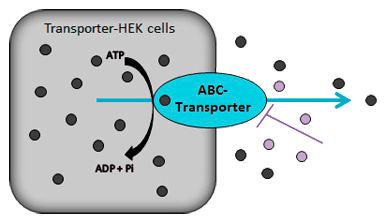
Efflux transporter assay for MDR1 and MRP2-HEK cells
Efflux assays are used to examine membrane transport by MDR1 (ABCB1) and MRP2 (ABCC2). Transporter- and control-HEK cells (monolayer) are preloaded with a fluorescence dye: Rhodamine123 is used for MDR1 and 5(6)-carboxy-2,’7′-dichloro-fluorescein (CDCF) for MRP2. The efflux of the fluorescent dye is measured in the absence and presence of increasing concentrations of a probe inhibitor or a test item.