hOAT3 (SLC22A8)
➦ The human organic anion transporter OAT3 (SLC22A8) is highly expressed at the basolateral membrane of proximal tubule cells in human kidneys, where it facilitates likewise OAT1 the first uptake step for renal secretion of a huge number of substrates. Preferentially, OAT3 mediate the transport of conjugated endogenous steroid hormones and several exogenous compounds like antibiotics, diuretics, NSAID (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), histamin-receptor2 blockers, antivirals, cytostatics and toxins. Therefore, the regulatory agencies decided that drugs eliminated significantly via the kidney have to be tested as potential inhibitors (substrates) for hOAT3.
| Main localization: | Kidney |
| Transporter assay: | Uptake transporter assay (potential inhibitors or substrates) |
| Probe substrates: | Estrone-3-sulfate |
| Probe inhibitors: | Indomethacin, probenecid |
| Regulatory relevance: | FDA and EMA guidance |
| Important interacting drugs: | Methotrexate, ochratoxin A, olmesartan, pitavastatin, pravastatin, rosuvastatin, probenecid, telmisartan, olmesartan, sulfasalazine, quinapril, ketoprofen, Losartan, furosemide, ibuprofen, indomethacin, bumetanide |
| From other species: | rOat3, mOat3 |
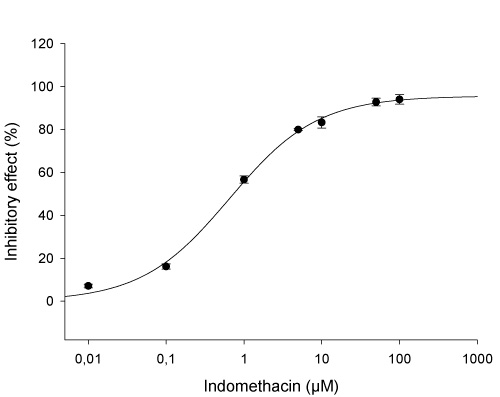
➦ Concentration dependent inhibition of hOAT3-mediated 3H-ES uptake by the probe inhibitor indomethacin