hOCT2 (SLC22A2)
➦ The polyspecific cation transporter OCT2 (SLC22A2) is most strongly expressed in kidney but it is also expressed in lung, skin, brain and choroid plexus. OCT2 mediates the first step uptake in proximal tubule epithelial cells in the renal secretion of several endogenous as well as exogenous substrates. OCT2 translocate physiological compounds like choline, dopamine, norepinephrine, epinephrine, serotonin, histamine, and testosterone. Biomedical impact: OCT2 facilitated translocation of platinum derivate could cause severe nephrotoxicity. Clinical relevance and Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) to renal uptake have been noted for OCT2. Therefore, the regulatory agencies decided that drugs eliminated significantly via the kidney have to be tested as potential inhibitors (substrates) for hOCT2.
| Main localization: | Kidney |
| Transporter assay: | Uptake transporter assay (potential substrates and inhibitors) |
| Probe substrates: | 1-methyl-4-phenyl-pyridinium (MPP), metformin |
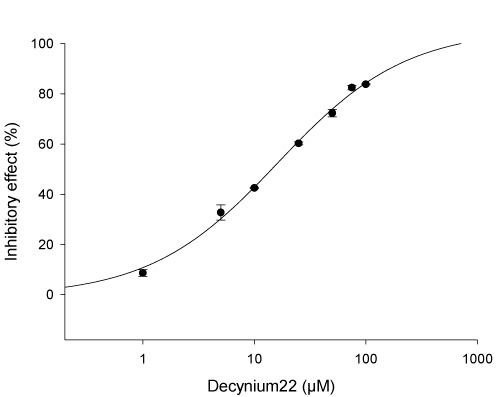
| Probe inhibitors: | Decynium22, quinine, quinidine |
| Regulatory relevance: | FDA, EMA, PDMA guidance |
| Important interacting drugs: | Metformin, quinidine, quinine, memantine, amantadine, ranitidine, oxaliplatin, cisplatin, cimetidine, fomatidine, amiloride, berberine |
| From other species: | rOct2, mOct2 |
➦ Concentration dependent inhibition of hOCT2-mediated MPP uptake by the probe inhibitor decynium22