hPEPT2(SLC15A2)
➦ The human peptide transporter 2 (PEPT2; SLC15A2) is mainly located in S2- and S3-segment of proximal tubule cells, although expression has also been observed in neurons, astrocytes, choroid plexus epithelial cells, bronchial epithelial cells, alveolar pneumocytes, mammary gland and spleen. PEPT2 operates as H+-coupled symporter of di- and tripeptides. PEPT2 reabsorbs renally filtered drugs from tubular fluid into proximal tubules, thereby affecting the systemic pharmacokinetics of several drugs. Substrates of PEPT2 include many important drug classes, including antivirals, β-lactam antibiotics, and angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors. One of the most commonly used reference substrates of the H+/peptide cotransporter is also glycylsarcosine (Gly-Sar). PEPT2 possess tenfold higher affinity for Gly-Sar than PEPT1.
| Main localization: | Kidney, brain |
| Transporter assay: | Uptake transporter assay (potential substrates and inhibitors) |
| Probe substrates: | Glycylsarcosine (Gly-Sar) |
| Probe inhibitors: | Losartan, TYR-PHE |
| Regulatory relevance: | − |
| Important interacting drugs: | Cefaclor, enalapril, bestatin, amoxicillin, 5-aminolevulinic acid, carnosine, cephalexin, losartan, valsartan |
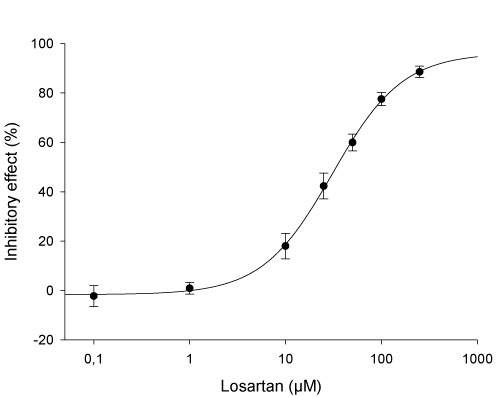
➦ Concentration dependent inhibition of hPEPT2-mediated Gly-Sar uptake by the probe inhibitor losartan