Methods
➦ Using genetically modified human kidney cells, we conduct interaction studies of drugs with specific transporter proteins. According to the ICH M12 guideline and recommendations from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), European Medicines Agency (EMA), and Japanese Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA), the characterization of clinically relevant drug transporters is becoming increasingly important in the drug approval process.
To characterize drug transporter interaction we provide the following assays:
Inhibition Assay
 Probe substrate (radio-labeled, non-labeled, fluorescent)
Probe substrate (radio-labeled, non-labeled, fluorescent)
 Test item as an inhibitor
Test item as an inhibitor
Substrate Assay
 Test item as a substrate (radio-labeled, non-labeled, fluorescent)
Test item as a substrate (radio-labeled, non-labeled, fluorescent)
 Probe inhibitor
Probe inhibitor
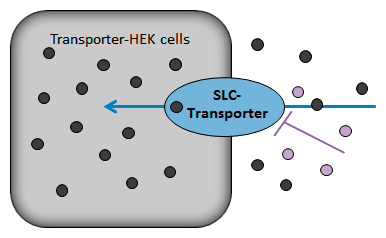
Uptake transporter assay for all SLC-Transporters
For the transporter assay, the SLC transporter is stably overexpressed in a suitable cell system, such as HEK293 cells. The cells are then incubated with a labeled or fluorescent substrate specific to the transporter. After a defined uptake period, intracellular accumulation of the substrate is measured using fluorescence, radioactivity, or LC-MS. Controls without transporter expression or with inhibitors are included to determine specificity. The data are analyzed to quantify transporter activity, typically by calculating uptake rates or kinetic parameters.
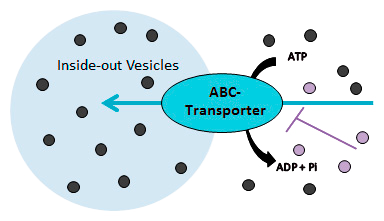
Vesicle based transporter assay for MDR1, BCRP, BSEP and MRPs
Membrane vesicles with an inside-out orientation are prepared from transporter-expressing HEK cells and control HEK cells. These vesicles are used to measure the ATP-dependent direct uptake of a substrate, which can be either a probe substrate or a test compound. Uptake is assessed in the absence and presence of an inhibitor, such as a probe inhibitor or test item, using the rapid filtration method. This vesicle-based approach is particularly suitable for low-permeability substrates, as compounds with moderate to high permeability are poorly retained.
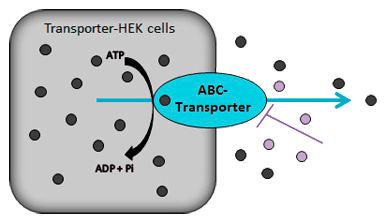
Efflux transporter assay for MDR1 and MRP2-HEK cells
Efflux assays are used to examine membrane transport by MDR1 (ABCB1) and MRP2 (ABCC2). Transporter- and control-HEK cells (monolayer) are preloaded with a fluorescence dye: Rhodamine123 is used for MDR1 and 5(6)-carboxy-2,’7′-dichloro-fluorescein (CDCF) for MRP2. The efflux of the fluorescent dye is measured in the absence and presence of increasing concentrations of a probe inhibitor or a test item.